Chapter 3: Key Trading Terminology and Concepts Demystified

TL;DR
- Understand Bid/Ask Price and Spread
- Trading Volatility and Volume
- Different Order Type
- Leverage and Margin Trading
- Slippage and Order Execution
Disclaimer: I am not a financial advisor. The content for this article is purely for educational/research purposes only and is merely based on my personal opinions.
Please note: There will be affiliate links in this article. But it will only benefit both of us. If you do not wish to participate under my affiliate links, please feel free to Google them separately. Cheers!
For Experienced traders only
Skip the basics and head straight to the real meat of our blog! [A Step-by-Step Breakdown of My Unique Trading Strategy] Delve into our main strategy guide and take your trading skills to the next level. No need to dwell on the fundamentals – let's fast-track to the valuable insights that can elevate your trading game. Click the link above now and immerse yourself in the strategy that matters most. It's time to master the markets like never before!
To navigate the world of trading successfully, it's essential to have a solid understanding of key trading terminology and concepts. In this blog post, we will explore and demystify some of the fundamental terms and concepts that every trader should be familiar with. Let's dive in!
Bid/Ask Price and Spread
Bid and ask prices are fundamental to understanding the pricing of financial assets in a market. Here's what you need to know:
Bid Price
The bid price represents the highest price at which buyers are willing to purchase an asset at a given moment.
Ask Price
The asking price represents the lowest price at which sellers are willing to sell an asset at a given moment.
Spread
The spread is the difference between the bid and ask prices. It represents the transaction cost and liquidity of the market. A narrow spread indicates high liquidity, while a widespread suggests lower liquidity.
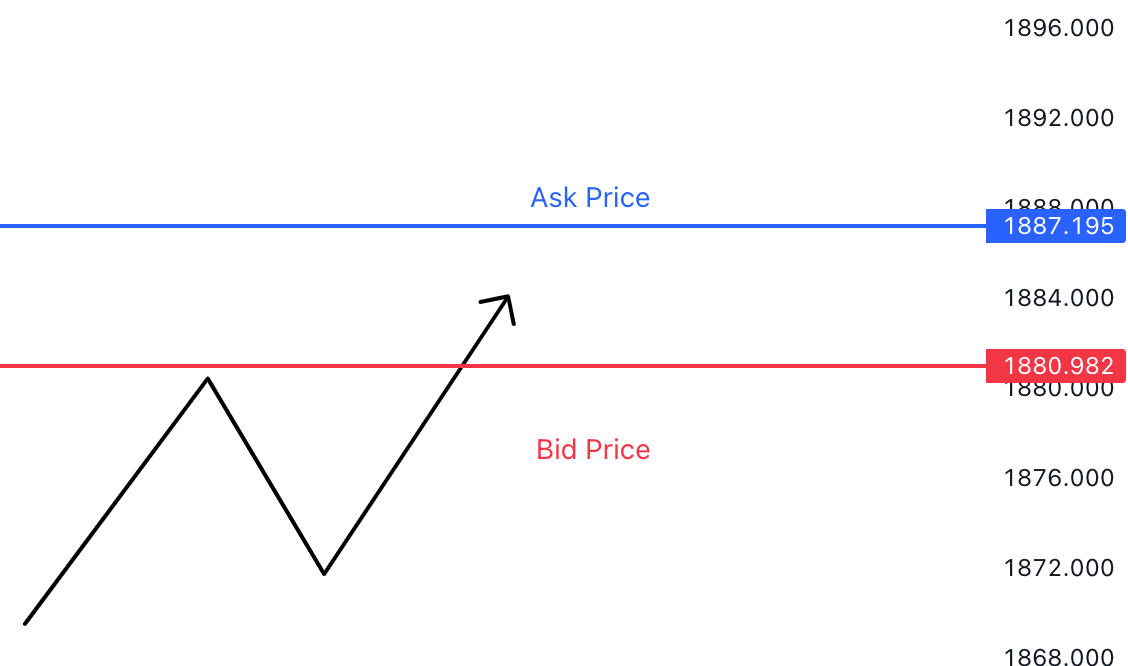
Understanding bid/ask prices and the spread helps traders assess the cost of entering or exiting a trade and provides insights into market dynamics and supply-demand imbalances.
At any point in time, there will be Bid/Ask price. If you intend to sell, you can only sell at Ask Price, slightly above the mean price. If you intend to buy, you can only buy at Bid Price, slightly below the mean price.
Volatility and Volume
Volatility and volume are two critical factors that impact trading decisions and strategies. Let's explore their definitions and significance:
Volatility
Volatility refers to the measure of price fluctuations or the degree of price variability of an asset over a specific period. High volatility implies large price swings, while low volatility suggests smaller price movements. Traders often seek volatility as it presents potential profit opportunities.
Volume
Volume represents the total number of shares, contracts, or units of an asset traded within a given period. It provides insights into the liquidity and interest in a particular asset. High trading volume indicates increased market activity and may confirm the validity of price moves.
Understanding volatility and volume helps traders identify suitable assets, gauge market sentiment, and select appropriate trading strategies that align with market conditions.
Order Types
Order types allow traders to specify the conditions and instructions for executing trades. Here are some common order types:
Market Order
A market order is an instruction to buy or sell an asset at the prevailing market price. It guarantees execution but not the specific price.
Limit Order
A limit order allows traders to set a specific price at which they are willing to buy or sell an asset. The trade will only be executed if the market reaches the specified price.
Stop Order
A stop order becomes a market order once the asset reaches a specified stop price. It is commonly used as a risk management tool to limit potential losses or protect profits.
Conditional Order
A conditional order is triggered based on predefined conditions, such as price movements or the occurrence of specific events. This order type allows for more advanced and automated trading strategies.
Understanding order types empowers traders to execute trades with precision and tailor their strategies based on specific market conditions and objectives.
Leverage and Margin Trading
Leverage and margin trading enables traders to control positions larger than their account balance. Here's what you need to know:
Leverage
Leverage amplifies the exposure to an asset by borrowing funds from a broker. It allows traders to control a more substantial position with a smaller capital outlay. However, leverage magnifies both profits and losses.
Margin Trading
Margin trading involves borrowing funds from a broker to finance a trading position. Traders are required to deposit a margin (a percentage of the total position value) as collateral. It enables traders to participate in larger trades with limited upfront capital.
Leverage and margin trading can enhance potential returns but also increase risk. Traders must carefully assess the risks and use appropriate risk management techniques when employing leverage and margin.
Slippage and Order Execution
Slippage and order execution are important considerations when executing trades. Let's explore their definitions and significance:
Slippage
Slippage refers to the difference between the expected price of a trade and the actual executed price. It can occur due to market volatility, liquidity issues, or delays in order execution. Slippage can result in trades being executed at a less favourable price than anticipated, impacting profitability.
Order Execution
Order execution is the process of converting a trading order into a completed trade. It involves the broker or exchange matching the buy and sell orders to facilitate the transaction. Efficient and timely order execution is crucial for traders to enter or exit positions at desired prices.
Understanding slippage and order execution help traders manage expectations, implement appropriate risk management measures, and choose brokers or platforms that offer reliable and efficient order execution.
Key Note
When trading in the financial market, such as forex, stocks, or options, it is crucial to factor in the spread cost. Large spreads and market volatility can lead to slippage, but some good practices can help minimize the impact. Incorporate spreads into the entry and stop loss levels, choose a reliable broker, and stick to a consistent trading strategy to avoid bad trades caused by excessive spread or slippage.
Endnote
Understanding key trading terminology and concepts is essential for traders to navigate the markets with confidence and make informed decisions. In this blog post, we explored bid/ask prices, spread, volatility, volume, order types, leverage, margin trading, slippage, and order execution. By familiarizing yourself with these concepts, you can enhance your trading skills, manage risks effectively, and develop strategies that align with market conditions. Remember, continuous learning and staying updated with market trends and developments are key to success in the dynamic world of trading.




